Imagine cultivating your favorite plants without the need for soil, right in your home or garden, using just water, nutrients, and innovative systems. Welcome to the world of hydroponics, an age-old cultivation technique revolutionized by modern technology. Hydroponics has become a go-to method for growing plants more efficiently, producing faster and higher yields, and enabling year-round gardening regardless of location.
Whether you’re an urban dweller or a green-thumb enthusiast, hydroponics offers flexible solutions tailored to your needs. This guide will cover the fundamentals of hydroponics, its types, and practical steps to get you started. Let’s dive into this soil-free revolution!
Table of Contents
Why Choose Hydroponics for Gardening?
Hydroponics is rapidly transforming how we grow plants. From hobbyists to commercial farmers, this innovative method appeals to all. Here’s why:
1. Water Efficiency
- Hydroponics uses up to 90% less water compared to traditional gardening.
- Water is recirculated, minimizing waste—a significant advantage in arid or water-scarce regions.
2. Faster Growth and Higher Yields
- Plants grow 25–50% faster with optimized delivery of water, nutrients, and oxygen directly to their roots.
- Shorter growth cycles and higher productivity make hydroponics ideal for home gardeners and commercial setups alike.
3. Space Optimization
- Vertical hydroponic systems allow you to grow more plants in less space, making it perfect for urban gardening or indoor setups.
- Compact systems fit easily into balconies, kitchens, or greenhouses.
4. Controlled Environment
- You control nutrient levels, water supply, and light exposure.
- Hydroponic systems reduce dependency on unpredictable weather and soil conditions, ensuring a consistent harvest.
5. Fewer Pests and Weeds
- No soil means no weeds, and fewer pests mean minimal pesticide use.
- This results in healthier, cleaner produce.
6. Year-Round Gardening
- With hydroponics, you can cultivate fresh produce regardless of the season, providing a continuous supply of herbs, vegetables, and fruits.
Types of Hydroponic Systems: Which One Is Right for You?
Hydroponic systems come in several forms, each catering to specific plants, spaces, and goals. Below, we’ll break down the six main types, drawing from proven methods used globally.
1. The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
How It Works:
- A shallow stream of nutrient-rich water flows through a slightly tilted channel or gutter system.
- Plant roots are placed in small openings along the channel, allowing them to come into direct contact with the flowing nutrient solution.
- Excess solution is collected at the end of the channel and recirculated using a pump.
Key Components:
- Channels: Made from materials like PVC or food-grade plastic, these channels need to be slightly sloped to facilitate water flow.
- Water Pump: Ensures a steady circulation of the nutrient solution through the system.
- Reservoir: Holds the nutrient solution and allows for pH and nutrient adjustments.
- Nutrient Solution: A precise mix tailored to the plants’ requirements.
- Support Structures: Net pots or sponges to hold plants above the nutrient film.
Benefits:
- Efficiency: Minimal water and nutrient wastage due to recirculation.
- Scalability: Can accommodate large or small-scale operations.
- Space-Saving: Compact design is ideal for urban and indoor gardening.
Best Plants for NFT:
- Lettuce
- Spinach
- Basil
- Other lightweight greens
Drawbacks:
- Not suitable for heavy fruiting plants like tomatoes due to limited root support.
- Requires precise monitoring to prevent pump or power failures that could disrupt nutrient delivery.
- Needs regular cleaning to avoid algae buildup in the channels. The NFT system is a widely-used hydroponic method, especially for lightweight crops like lettuce and herbs.
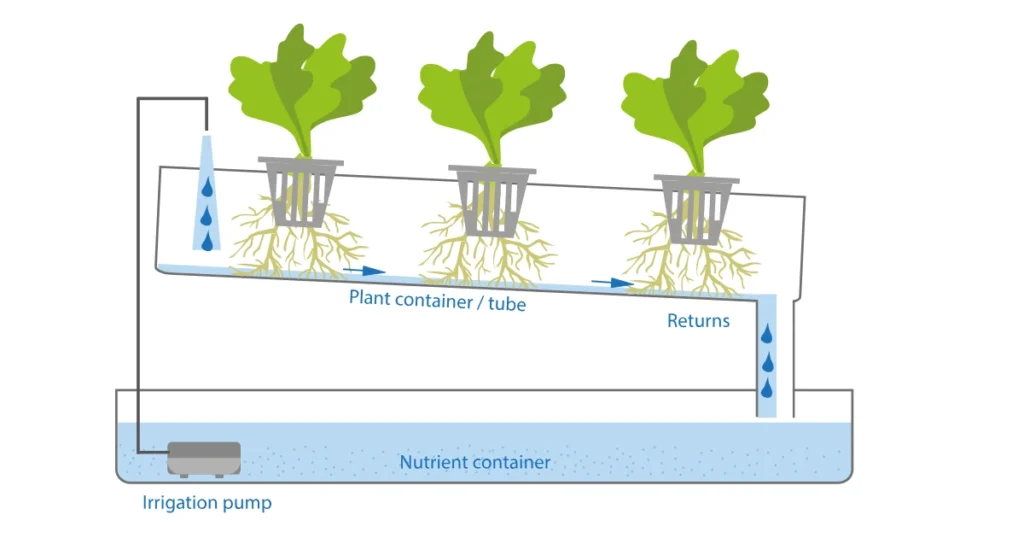
2. Deep Water Culture (DWC)
DWC is one of the simplest systems, perfect for beginners and hobbyists.
How It Works:
- Plant roots are suspended in nutrient-enriched water.
- Air pumps provide oxygen through air stones to prevent root suffocation.
Benefits:
- Rapid Growth: Constant nutrient access accelerates development.
- Low Maintenance: Fewer components make it user-friendly.
- Budget-Friendly: Affordable materials like buckets and air stones.
Best Plants for DWC:
- Kale
- Lettuce
- Peppers
Drawbacks:
- Water temperature control is critical.
- Limited scalability for larger operations.
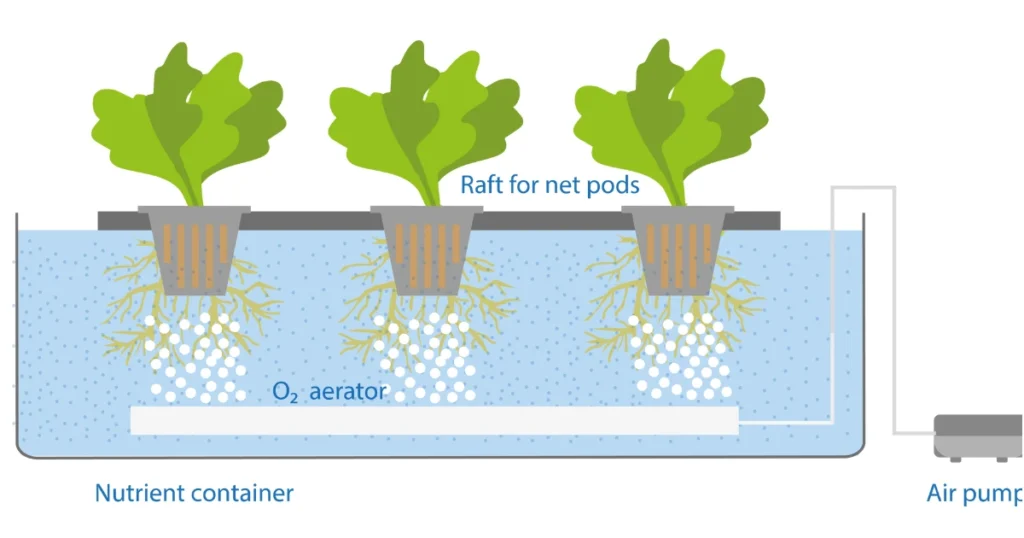
3. Drip System
The drip system provides flexibility and control, making it a popular choice for commercial growers.
How It Works:
- Nutrient solution drips onto the plant roots through emitters.
- Excess water drains back into the reservoir for reuse.
Benefits:
- Versatility: Supports a wide range of plants.
- Precise Control: Adjustable drippers cater to different plant needs.
- Water Conservation: Minimal waste with closed-loop systems.
Best Plants for Drip Systems:
- Tomatoes
- Strawberries
- Cucumbers
Drawbacks:
- Clogged emitters require frequent cleaning.
- Initial setup can be complex.
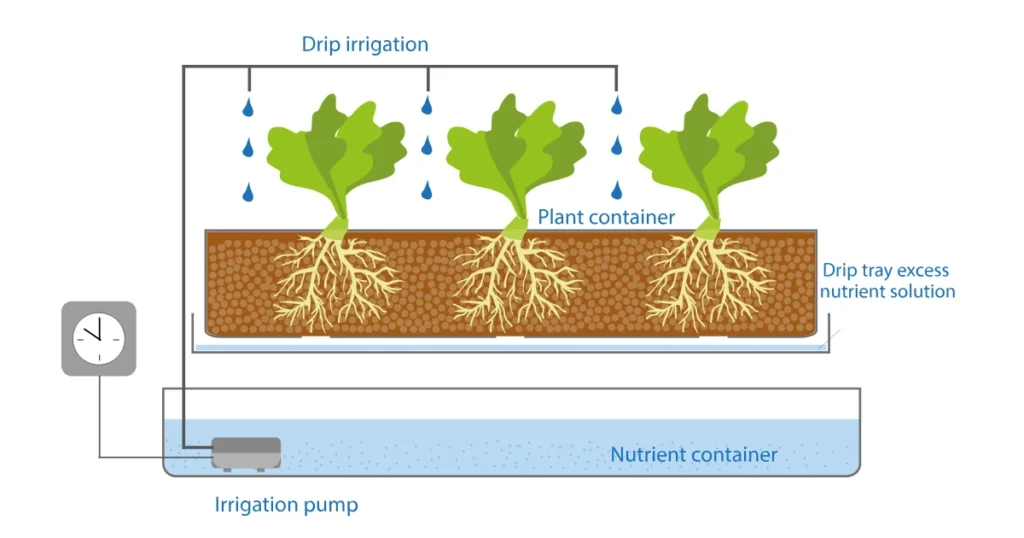
4. Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain)
This dynamic system mimics nature’s watering cycles, encouraging robust growth.
How It Works:
- A pump floods the grow bed with nutrient solution at set intervals.
- The nutrient solution flows back to the reservoir using gravitational force.
Benefits:
- Oxygen Boost: Alternating cycles oxygenate roots effectively.
- Adaptability: Suitable for various plant sizes and types.
- Reusability: Works well with multiple growing mediums.
Best Plants for Ebb and Flow:
- Herbs
- Leafy greens
- Strawberries
Drawbacks:
- Requires precise timing and monitoring.
- Pump failures can cause plant stress.
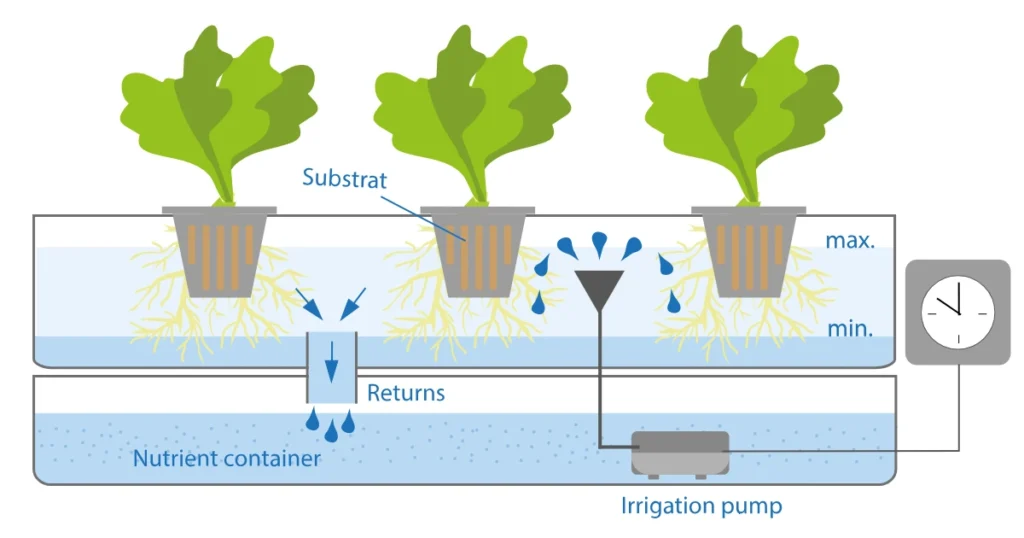
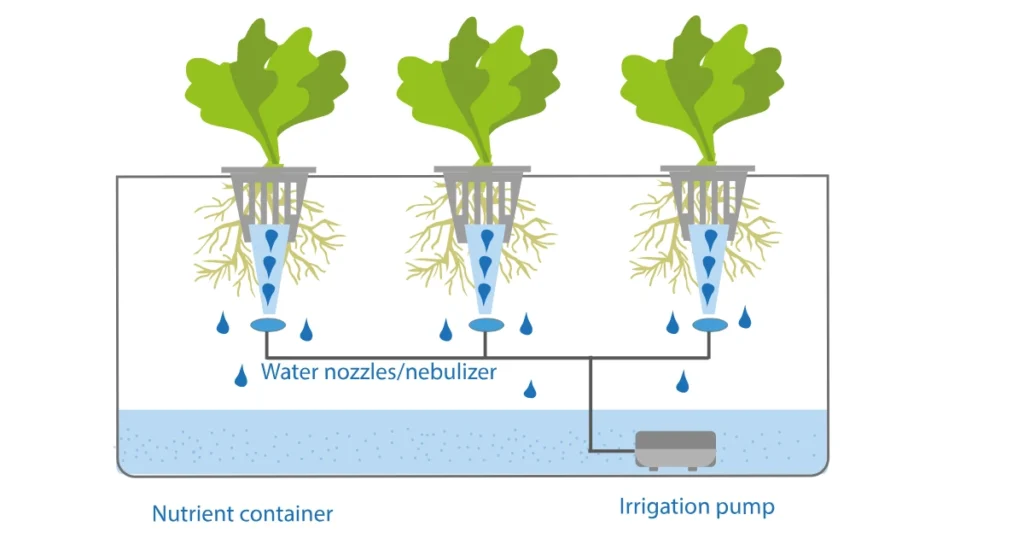
5. Aeroponics
Aeroponics takes hydroponics to the next level, offering unparalleled efficiency and innovation.
How It Works:
- Roots hang freely in the air and are sprayed with a fine mist of nutrients.
- High-pressure pumps deliver the mist at regular intervals.
Benefits:
- Maximum Efficiency: Uses the least water and nutrients.
- Faster Growth: High oxygen levels boost plant metabolism.
- Space-Saving: Perfect for vertical farming setups.
Best Plants for Aeroponics:
- Lettuce
- Herbs
- Strawberries
Drawbacks:
- High initial costs.
- Requires advanced knowledge and maintenance.
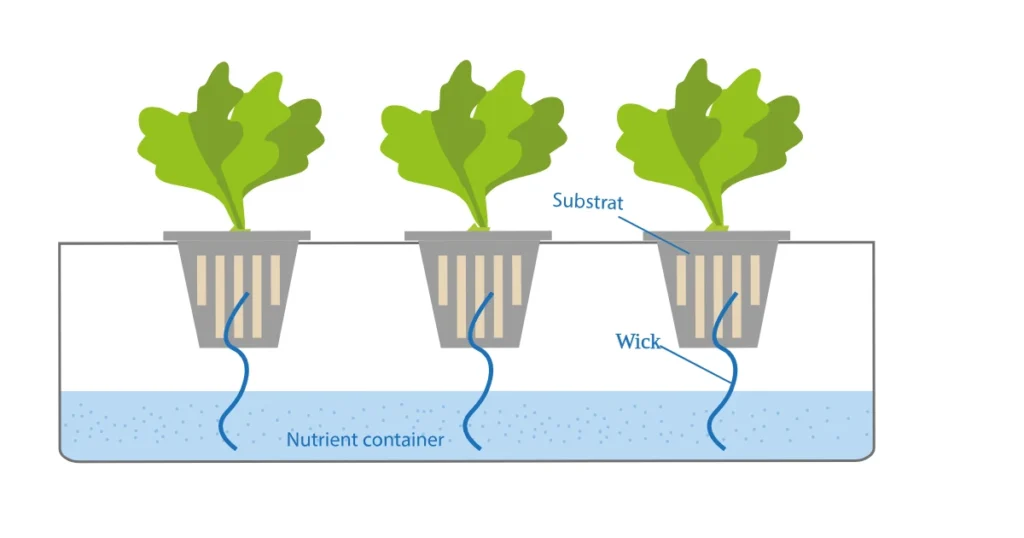
6. Wicking System
Simple, sustainable, and low-maintenance, the wicking system is great for beginners.
How It Works:
- A wick transports the nutrient solution from the reservoir directly to the plant’s roots.
- Works best with absorbent growing mediums like coconut coir, perlite, or vermiculite, which efficiently transfer moisture to plants.
Benefits:
- Low Cost: Minimal components required, such as wicking materials, a reservoir, and a simple grow tray.
- Ease of Use: No pumps or timers necessary, making it a great option for hands-off gardening.
- Reliability: Ideal for remote locations or areas with limited access to electricity.
Best Wicking Materials:
- Cotton: Readily available and highly absorbent.
- Nylon Rope: Durable and resistant to rotting.
- Felt Strips: Excellent for consistent water delivery.
- Capillary Matting: Designed specifically for gardening purposes and widely accessible in gardening stores.
Best Plants for Wicking:
- Herbs
- Leafy greens
Drawbacks:
- Not suitable for water-intensive or large plants, as the wicking mechanism may not supply enough moisture for their needs.
- Over time, salt buildup can occur in the wicks, requiring periodic cleaning or replacement to ensure consistent performance.
Choosing the Right Hydroponic System
Now that you know the types, here are a few factors to consider when selecting the best hydroponic system:
- Plant Type: Light crops thrive in NFT, while heavier plants need drip or ebb and flow systems.
- Space Availability: Small spaces favor DWC or wicking systems.
- Budget: Start with cost-effective setups like DWC or wicking.
- Skill Level: Beginners should opt for simpler systems like wicking or DWC before advancing.
| System Type | Ideal For | Difficulty Level | Initial Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| NFT | Herbs, lettuce | Intermediate | Medium |
| DWC | Leafy greens | Easy | Low |
| Drip System | Fruiting plants | Advanced | High |
| Ebb and Flow | Mixed plants | Intermediate | Medium |
| Aeroponics | Herbs, strawberries | Advanced | High |
| Wicking | Herbs, greens | Easy | Low |
Getting Started with Hydroponics
Step 1: Select the Right System
- For beginners: Start with DWC or a Wick System for simplicity.
- For advanced growers: Experiment with NFT or Aeroponics for higher efficiency.
Step 2: Choose Your Plants
- Leafy Greens: Lettuce, spinach, kale.
- Herbs: Basil, cilantro, mint.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Tomatoes, cucumbers, strawberries.
Step 3: Set Up Lighting
If growing indoors, use LED grow lights to provide full-spectrum light essential for plant photosynthesis.
Step 4: Maintain the Nutrient Solution
- pH range: 5.5–6.5.
- Keep an eye on the Electrical Conductivity (EC) levels to maintain the right balance of nutrients.
Step 5: Monitor and Maintain
Check for algae growth, nutrient imbalances, and pump functionality regularly to ensure healthy plant growth.
Hydroponic Recipes for Beginners
| Plant Type | Optimal pH | Nutrient Range (PPM) | Growing Time (Weeks) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lettuce | 5.5–6.0 | 560–840 | 6–8 |
| Tomatoes | 5.8–6.5 | 1400–3500 | 8–12 |
| Basil | 5.5–6.5 | 700–1120 | 5–7 |
| Strawberries | 5.5–6.0 | 560–840 | 10–14 |
For more gardening tips follow us on Pinterest
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are 3 disadvantages of hydroponics?
High Initial Cost – Setting up hydroponic systems requires investment in equipment, nutrients, and infrastructure.
Technical Knowledge Needed – Maintaining correct nutrient balance, pH levels, and system cleanliness requires ongoing monitoring and expertise.
Vulnerability to Power Outages – Many hydroponic systems rely on pumps and artificial lighting, so interruptions can quickly harm plants.
Is hydroponic food healthier?
Hydroponic food is often equally nutritious as soil-grown food and sometimes richer in certain nutrients due to optimized growing conditions. Because hydroponics avoids soil contaminants and pesticides, it can produce cleaner, safer crops. However, the nutritional quality ultimately depends on the specific nutrient solutions and plant varieties used.
What is the main problem in hydroponics?
The main challenge in hydroponics is maintaining the right nutrient and pH balance consistently. Imbalances or contamination can cause nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, affecting plant health. Additionally, system failures like pump breakdowns can rapidly damage plants due to their dependence on constant water flow.
Are hydroponics sustainable?
Yes, hydroponics can be highly sustainable. It uses up to 90% less water than traditional soil farming, reduces land use, and allows for local, year-round food production, cutting down food miles and emissions. However, sustainability depends on factors like energy sources, nutrient management, and materials used in the system
1. Which hydroponic system is best for beginners?
The Deep Water Culture (DWC) system is ideal for beginners due to its simplicity and low maintenance.
2. Can hydroponic plants grow without sunlight?
Yes, hydroponic plants can thrive indoors with the help of LED grow lights, which provide the necessary light spectrum for photosynthesis.
3. Is hydroponics better than traditional gardening?
Hydroponics is more efficient, environmentally friendly, and space-saving compared to traditional gardening. It allows faster plant growth and eliminates soil-related challenges.
4. How often should I change the nutrient solution?
Replace the nutrient solution every 2–3 weeks to prevent nutrient imbalances and ensure optimal plant health.
5. Can I grow root vegetables in hydroponics?
Yes, root vegetables like carrots and radishes can be grown in systems like Ebb and Flow with appropriate adjustments.
Conclusion
Hydroponics offers you a modern, efficient, and rewarding way to garden. Start small, learn the basics, and gradually expand your system. With the right setup and care, you’ll soon enjoy thriving plants and bountiful harvests.
Happy gardening!

3 thoughts on “Your Ultimate Guide to 6 Hydroponic Systems: Benefits, and Setup”